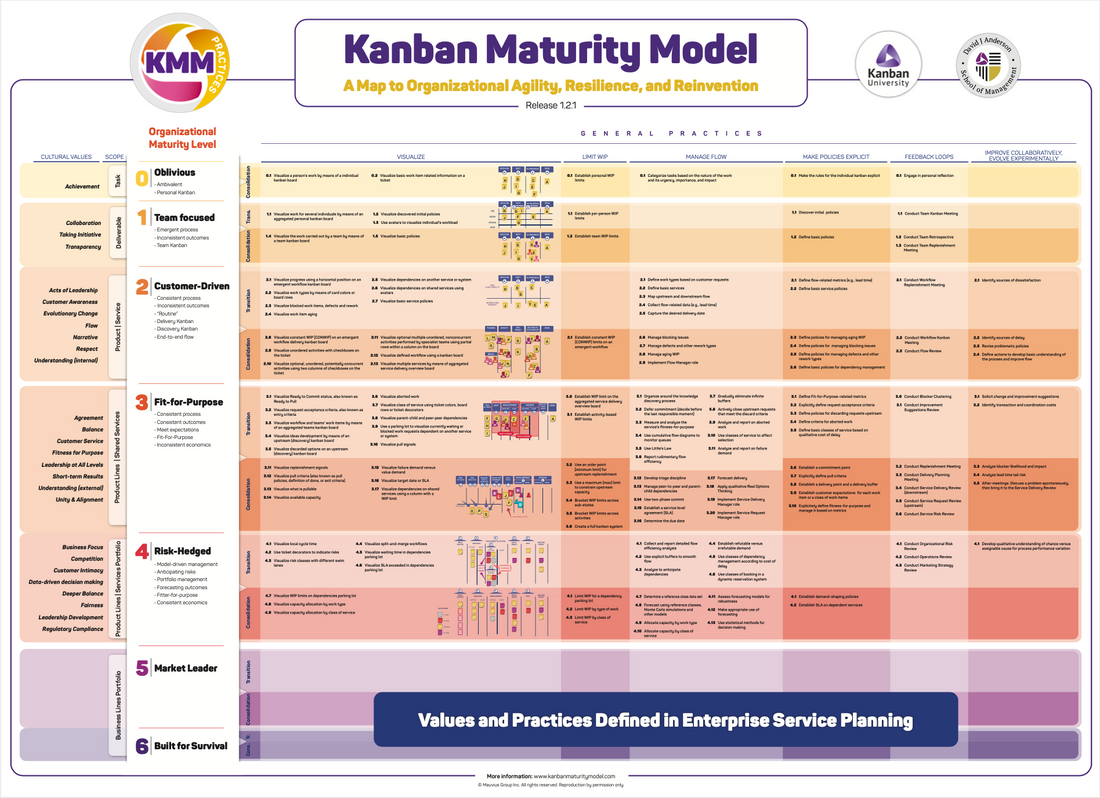
The Kanban Maturity Model (KMM) is a process-level improvement model with the Kanban Method. The KMM can be used to guide a process improvement across teams, departments, or entire organizations. It maps out 7 maturity levels and shows how to successfully deploy the Kanban Method to move from one level to another and greatly improve the economic performance of the business.
There is widespread thought that Kanban is just a board with columns and colored tickets. But the Kanban Method goes much beyond that. It can be used to manage the processes of the whole organization and the Kanban Maturity Model only proves that.
History
The Kanban Maturity Model emerged with the publication of the 1st edition of the book – “Kanban Maturity Model: Evolving Fit-For-Purpose Organizations” in 2018. This was the minimal viable product, that could be released to the market and it was mainly based on the authors` professional experience. From that time, the authors David J. Anderson and Teodora Bozheva spent 4 years refining, developing, and testing the model on the market.
The new second edition of the book, published in 2020, includes the results of the beta program that was running for more than a year to validate the Model. KMM’s new release maps more than 150 specific practices across 7 levels of organizational maturity and serves as a roadmap for consultants, coaches, or medium and large enterprise managers who want to transform and improve their business using the Kanban Method.
Read the whole KMM 2nd edition book online, get access to the entire library of Kanban posters, videos, learning modules with David Anderson, and more on Kanban+ (create your free account to explore the platform).
What the Kanban Maturity Model can help you with?
The Kanban Maturity Model addresses to development of the following organizational capabilities:
- Relief from overburdening
- Workforce cohesion and employee fulfillment
- Meeting customer expectations
- Delivering satisfaction to customers
- Defining and managing organizational identity and purpose
- Resilience to setbacks and market turbulence
- Predictable, sustainable economic performance and financial robustness
- Organizational agility
- Congruence of decision-making from top to bottom.
- Long-term survival
- Meaningful, institutionalized change that sticks.
The KMM is for businesses that aspire to superior agility, to deliver fit-for-purpose products and services, to delight customers, and to provide the security of long-term survival associated with mature businesses that consistently meet or exceed customer expectations.
The Kanban Maturity Model defines the following levels:
0 – Obvious
The organization is not aware of the need for a structured work process. Mostly they may visualize work on a personal level using a physical or online Kanban board. Applying Kanban on a team level is still difficult. Individuals are focused on personal achievements and getting things done, it is self-concentrated, and the level of trust is low.
1 – Teams-focused

Here team members have already acquired a habit of using Kanban. The need to move it to a team level is emerging, so the team creates its team`s board and moves its work from individual boards. Per-person swim lanes are introduced to visualize individual tasks, and the team agrees on initial policies. At this stage, we see such improvements as collaboration, work transparency, and taking initiative. This organization is now concentrated on deliverability and teamwork.
2 – Customer-driven

At this level, the team understands that Kanban helps to improve collaboration and brings transparency to a process. The need for a defined work process and service recognition emerge. The process, policies, and decision frameworks are already consistent, however, there is still inconsistency in the desired outcome. At this level we can see the acts of leadership and evolutionary change, establishing the flow, internal understanding, and respect. There is a basic understanding of demand and capability, the focus now is on product and service.
3 – Fit-For-Purpose

“No more heroes anymore”. At this level organization better understands the processes, workflow, policies, and decision frameworks and how they help to achieve better results. The process evolves from customer-driven to fit-for-purpose. The organization better meets its customers’ expectations, and better balances an upstream and downstream flow. The next step is to improve the consistency and predictability in front of customers, create actionable metrics, and shorten the lead time. The focus has changed to “Why do we exist?”, and the organization has started being more resilient.
4 – Risk-Hedged

The organization embraces a model-driven management approach to strategic planning that anticipates risks, predicts outcomes and results. This level introduces risk-hedging practices, data-driven decision-making frameworks, and the use of predictive models that improve overall business economics and robustness against unforeseen events. Here we can already observe deeper balance, fairness, customer intimacy, quantitative analysis, and dynamic scheduling.
5 – Market-Leader

The company is entirely “fit-for-purpose” from each stakeholder and end-user perspective. Now it is important to continually optimize the workflow, improve the efficiency and financial benefits maintain high quality and margins, minimize costs, and optimize the delivery rate. The focus now is on “how do we do things”, the organization is already showing its agility, workforce flexibility, equality of opportunity, and perfectionism.
6 – Built for Survival

This is a “built to last” level of organization. Such an organization can reinvent itself; it is antifragile and opts for long-term survival. It has congruent decision-making and is robust to external changes. It is mature enough to ask and assess such questions, as “Is the way we do things still competitive?”, “Are new technologies, processes, or methods becoming available that we should be adopting?”, and “Are we still offering the right products and services, or should we reinvent ourselves?”. These questions are strategic. A mature organization will keep its hands on the pulse of its business and will be able to establish the right capabilities to align with the broader company strategy.
Download the Kanban Maturity Model posters for free here.
How to learn about the Model?
There are several ways to learn the Kanban Maturity Model to be able to apply it to your organization. David J Anderson School of Management provides regular training where attendees learn how to understand the KMM and safely apply its principles to avoid one of two common failure modes in Kanban implementation: overreaching or false summit plateau. Those, who want to learn KMM in their language can choose their local trainer from Kanban University base.
For the ones, who are interested in learning about the KMM on their own, the Kanban Maturity Model book is available for purchase. To learn it online you can subscribe to the kanban.plus. It has a whole library of all KMM-related materials: all existing Kanban Maturity Model posters, connects them to corresponding book chapters, allows you to read all book chapter by chapter, and includes videos, infographics, articles, and case studies. You can also directly download any of the available assets.
Who would benefit from the Kanban Maturity Model:
First, the KMM is useful for Coaches. It explains practices, values, and cultural aspects to grow and evolve using the Kanban Method. KMM has practices related to relief of overburdening to make people collaborative in a team, between teams, on the organizational level, or in different business lines. It will help Coaches to understand where the organization is, where it wants to be, and how to move it forward toward its goal.
Second, Kanban practitioners can use it as a catalog and reference to the main Kanban Method aspects, practices, and principles and find enough information on how to implement them.
Third, it will help middle-level managers or Product/ Project Managers, Service Managers and Officers, Service lines, etc. to find practices to introduce the service orientation in their companies, which is fundamental for business agility.
Application
The Kanban Maturity Model makes it easier to implement the method at a large scale with greater confidence in successful outcomes. The case study described in chapter 4 of the KMM book, details the two-year-long experience of the Finance area of BBVA with the Kanban Maturity Model, guided by Teodora Bozheva, and shows the promising results of a 28% drop in management overhead in their internal finance division.
Another case study tells us a success story of Vanguard’s Kanban Maturity Model implementation. Vanguard is one of the world’s largest investment management companies. The KMM implementation resulted in 40% out of twenty-four teams, all of which were started with Vanguard’s default Scrum method, that decided to switch to Kanban. Nearly all these Kanban teams exhibited flow metrics that outperformed almost all Scrum teams. At the team’s level, system lead time and cumulative flow improved dramatically for the post-Scrum Kanban teams. The KMM implementation resulted in evident acts of leadership at every level. But the biggest compliment was when Vanguard Crewmates came up to Kanban teams and asked, “So, how do you deliver so much value so well?”. Especially when it came from Managers.
Explore the Kanban Maturity Model on Kanban+
Kanban+ is one source of truth when it comes to the Kanban Method and the Kanban Maturity Model. It is one platform that gathers all possible materials, taught and used by Kanban University. Create your free account now and get access to a set of free content such as posters, infographics, book chapters, and more. Improve your professional knowledge today!